




 Used by thousands of data scientists, engineers, business analysts, consultants, and healthcare professionals!
Used by thousands of data scientists, engineers, business analysts, consultants, and healthcare professionals!
| Comparison | |
|---|---|
|
Superintendent.app
Excellent for working with CSVs
|
Easy installation
Easy to use
Supports large files
Installed with a single click, the UI-based app is purposefully built for your productivity.
You can build your reports within seconds.
In addition, it supports large CSV files e.g. importing 1GB file in 10 seconds.
|
|
Spreadsheet apps
Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets
|
Easy installation
Easy to use
Supports large files
Spreadsheets like Excel and Google Sheets are clunky with SQL and don't support CSVs larger than 1 million rows.
|
|
Database tools
DBeaver and MySQL Workbench
|
Easy installation
Easy to use
Supports large files
This alternative requires a database setup and often offers a myriad of unnecessary functionalities (e.g. configuring database) that get in the way for users who work with CSVs.
|
|
Command-line tools
csvkit and q
|
Easy installation
Easy to use
Supports large files
This alternative often requires Python setup. Managing multiple CSVs and SQLs in a terminal is clunky.
While the tools don't impose a file size restriction, they are not performant when handling large files.
|
|
Databases
SQLite and DuckDB
|
Easy installation
Easy to use
Supports large files
Managing multiple CSVs and SQLs directly in a database's terminal is extremely clunky, even more clunky than using a command-line tool.
|
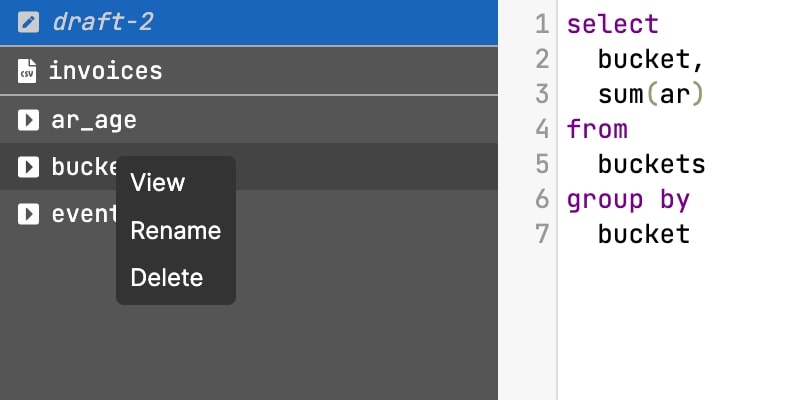
Make a draft, rename, delete, move tabs around, and re-run.
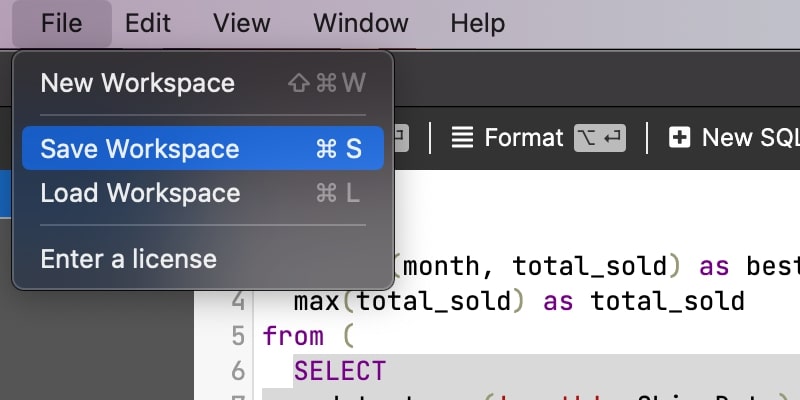
Load it back later, send it to your colleague. Never lose your work.
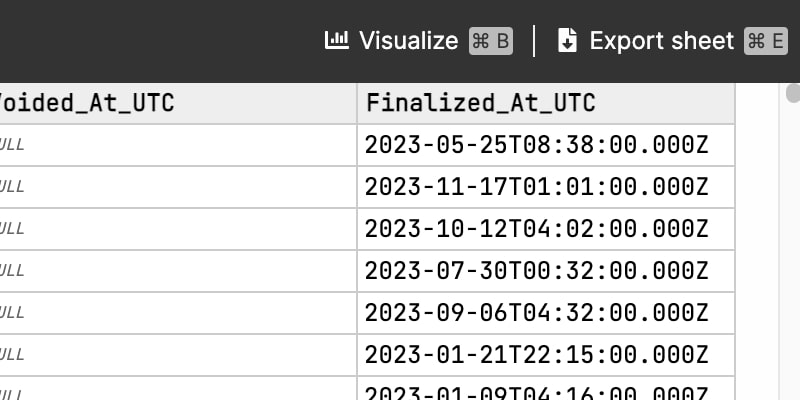
Once you finish, you can export your results to CSVs.
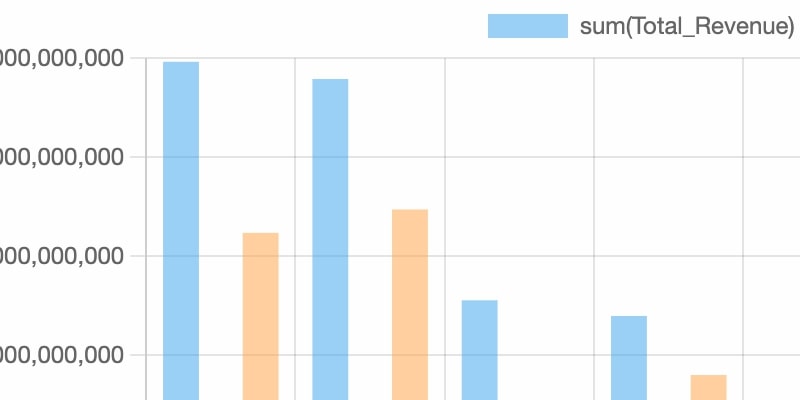
Visualie your results in line charts, bar charts, stacked bar charts, and pie charts.
Click on columns and press Ctrl+C to copy. Copy millions of cells or as much as your memory allows.

Highlight a part of SQL and see its result when you aren't sure what the SQL entails.
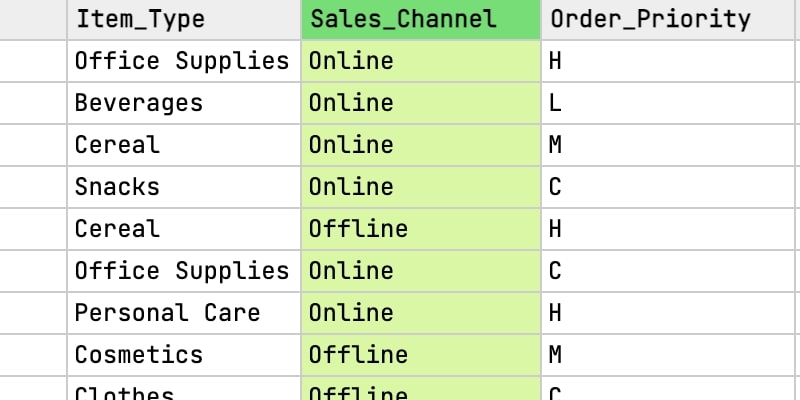
Click on multiple columns to sort ASC or DESC. Only one click away for your convenience.
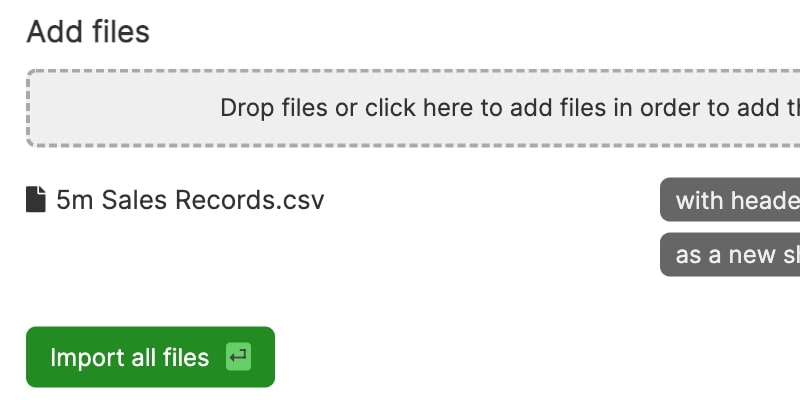
Just import CSV. The names and types are automatically handled for you.
Cool app to query CSV’s with SQL! superintendent.app
Handige tool! Superintendent, SQL-tool voor CSV bestanden superintendent.app
I use superintendent.app (made by @tanin) basically let's you run SQL on raw CSVs
¿Una aplicación o producto ha mejorado considerablemente tu trabajo del día a día? Empiezo yo: superintendent.app
superintendentは,読ませたCSVファイルをSQL使ってコネコネできるアプリ。SQL知ってる人は便利だと思う superintendent.app
I don't work with data analysis anymore, but jfc the potential for this thing is awesome. Well done, mate!
Or how to handle a large CSV in Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets?
Read more →This guide shows how to build the AR aging report based on Stripe reports using SQL.
Read more →Using Superintendent.app to analyze logs locally is faster and cheaper.
Read more →This guide shows how to extends SQLite to support richer date parsing and formatting.
Read more →